linalool
An abundant (~90%) essential oil of the leaves of Aniba rosaeodora [46, 47] that is used in the traditional medicine of the Peruvian and Brazilian Amazon for its effects on the central nervous system, such as :
Additionally, linalool has :
Several studies have demonstrated a gamma of anti-infectious activity like antiviral [54], antibacterial [55, 56, 57], antifungal [58, 59], and antileishmanial [55, 60, 61].
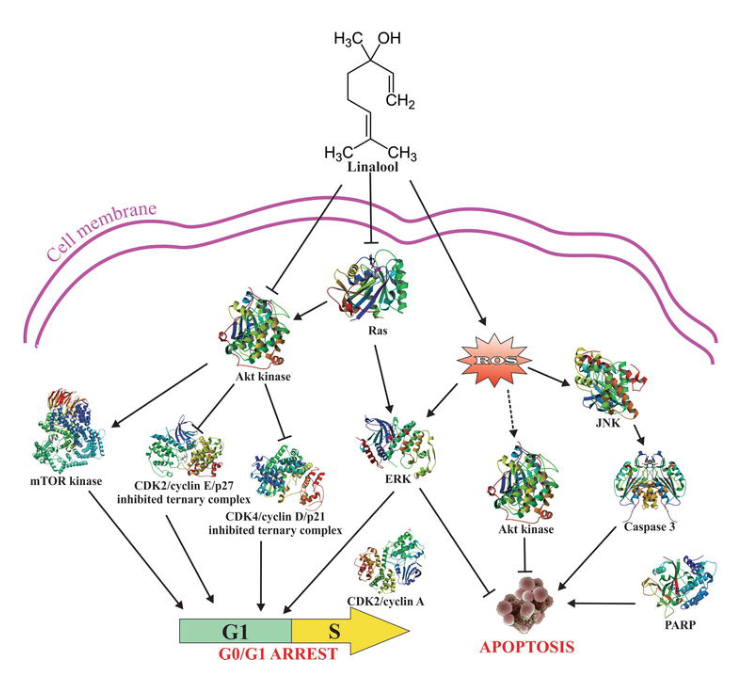
The anticancer mechanisms of action of linalool in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) HepG2 cells were recently revealed by Rodenak-Kladniew et al. [50] (Figure 4).
According to these researchers, linalool in a dose-dependently blocked cell proliferation by inducing G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, through Cdk4 and cyclin A downregulation, p21 and p27 upregulation, and apoptosis, characterized by mitochondrial membrane potential loss, caspase-3 activation, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage, and DNA fragmentation.
- sedative,
- anticonvulsant, and
- antidepressant
Additionally, linalool has :
- anti-inflammatory [49],
- anticancer [50, 51, 52],
- antihyperlipidemic,
- antinociceptive,
- analgesic,
- anxiolytic, and
- neuroprotective properties [53].
Several studies have demonstrated a gamma of anti-infectious activity like antiviral [54], antibacterial [55, 56, 57], antifungal [58, 59], and antileishmanial [55, 60, 61].
The anticancer mechanisms of action of linalool in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) HepG2 cells were recently revealed by Rodenak-Kladniew et al. [50] (Figure 4).
According to these researchers, linalool in a dose-dependently blocked cell proliferation by inducing G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, through Cdk4 and cyclin A downregulation, p21 and p27 upregulation, and apoptosis, characterized by mitochondrial membrane potential loss, caspase-3 activation, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage, and DNA fragmentation.
Figure 4. Anticancer mechanisms of action of linalool in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) HepG2 cells.